Introduction🔗
To take advantage of Lightrun’s functionality in your AWS Lambda function, you must deploy Lightrun’s agent library with your project. One of the ways to import the additional code (frameworks, SDKs, libraries, and more) into a Lambda function is to bundle the function with an AWS Lambda Layer.
In this tutorial, we will learn how to package the Lightrun Python agent into a Lambda layer. We will also demonstrate how to attach the Lambda layer to your AWS Lambda function in order to be able to import and use Lightrun in your project.
Note
These instructions are valid only for AWS Lambda functions deployed as a .zip file archive.
Prerequisites🔗
This tutorial assumes that you have:
- Created your Lightrun account.
- Created an AWS account.
- Installed and set up Docker on your local machine.
Create a Lambda layer🔗
AWS Lambda Layer is a .zip archive containing libraries, configuration files, dependencies, etc., that you can import at runtime into your Lambda function. To create an AWS Lambda layer for the Lightrun Python agent, we must compile the Lightrun Python agent into a .zip archive and then upload the .zip file archive to AWS via the AWS console or with the AWS CLI.
Compile the Lightrun Python agent into a .zip archive.🔗
The first step when creating an AWS Lambda layer is to bundle the layer’s content into a .zip file archive. To set up a .zip file for the Lightrun Python agent, first, create a new directory that we will use to store the dependencies that will go into the Lambda layer.
mkdir python_lambda_layer
cd python_lambda_layer
Then add a requirements.txt file with the following content to the folder.
lightrun
To use the Lightrun Python agent in our AWS lambda function, we must deploy an agent version that is compatible with the AWS Lambda execution environments. AWS provides two computer processors (arm64 and x86_64) and these Python runtimes (Python 3.9, Python 3.10, and Python 3.11) for running AWS Lambda functions.
In this tutorial, we will install a Python agent with the Lambci docker-lambda image. Lambci docker-lambda provides a sandbox environment replicating the AWS Lambda execution environment almost identically. With the provided sandbox environment, we can compile a Python agent that is compatible with the AWS architecture and runtimes.
Run the following command to install the Lightrun Python agent in the python_lambda_layer folder with the Lambci docker-lambda image. For this tutorial, we will be using x86_64/python3.9 as our preferred Lambda architechture and runtime environment.
docker run --rm -v $(pwd):/foo -w /foo lambci/lambda:build-python3.9 \
pip install -r requirements.txt -t python/lib/python3.9/site-packages/; exit
Note
Installed dependencies in a Python Lambda layer must be stored in a python/{our libraries} or python/lib/{python-version}/site-packages/{our libraries} file path for the dependencies to be discovered by a Python Lambda function. You can learn more about Lambda layer paths here.
A python/lib/python3.9/site-packages/<lightrun python agent> will be added to the python_lambda_layer folder if the installation was successful.
Package the installed dependencies into a .zip file with the following command.
zip -r layers.zip python > /dev/null
A layers.zip file will be added to the python_lambda_layer folder.
Create a Lambda layer for the Lightrun Python agent🔗
After compiling the Lightrun Python agent into a .zip file archive. The next step will be to create our AWS Lambda layer. We can deploy the .zip file to AWS in two ways:
Create a Lambda layer from the AWS console🔗
To create an AWS Lambda layer from your AWS console.
- Navigate to the AWS Lambda console, and open the Layers page of the console.
- Click Create Layer.
- Specify a name for the new Lambda Layer.
- Upload the
layers.zipfile. - Select the compatible architecture and runtime for your .zip file (we installed our dependencies with the x86_64 architecture and python3.9 as the preferred runtime environment).
- Click Create.
The new Lambda Layer is now available to your Python Lambda functions.
Create a Lambda layer with the AWS CLI🔗
Note
The following instructions assume that you have the AWS CLI installed on your local machine. Follow the instructions here to install and set up the AWS CLI on your local machine if you haven’t already installed it
Create the AWS Lambda layer with the AWS CLI with the following command.
aws lambda publish-layer-version --layer-name 'Lightrun_Package_python' --compatible-runtimes 'python3.9' --zip-file fileb://layers.zip --region us-east-1
Change 'Lightrun_Package_python' to your preferred layer name, change us-east-1 to your preferred region, and 'python3.9' to your desired Python runtime environment.
If the deployment was successful, you should get a similar response to this in your terminal.
{
"Content": {
"Location": "<aws_location_key>",
"CodeSha256": "hqfw2fMHXzqnYZ+S+zc1ZgKZhsnJzijxtbhDIqVVm9U=",
"CodeSize": 7911221
},
"LayerArn": "<layers_arn>",
"LayerVersionArn": "<layers_version_arn>",
"Description": "",
"CreatedDate": "2022-06-18T07:44:12.702+0000",
"Version": 4,
"CompatibleRuntimes": [
"python3.9"
]
}
Important
Note the LayerVersionArn key that I highlighted above. We will use the key to bundle the Python agent Lambda layer into our Lambda functions if we want to deploy our Lambda function directly from the AWS CLI.
Share the Lambda layer to your application🔗
Now that we have created a Lambda layer for the Lightrun Python agent, the next step will be to add the Lambda layer to our Python Lambda function to be able to debug the Lambda function with Lightrun. We can do this in two ways.
- Add the Lambda layer to a Lambda function from the AWS Console.
- Add the Lambda layer to a Lambda function with the AWS CLI.
Add the Python agent Lambda layer to your Lambda function from the AWS Console🔗
If you have already deployed your Python function to AWS, you can attach the Lambda layer to the Lambda function from your AWS Console. First open the Functions page in your AWS Lambda console, and select the relevant Lambda function.
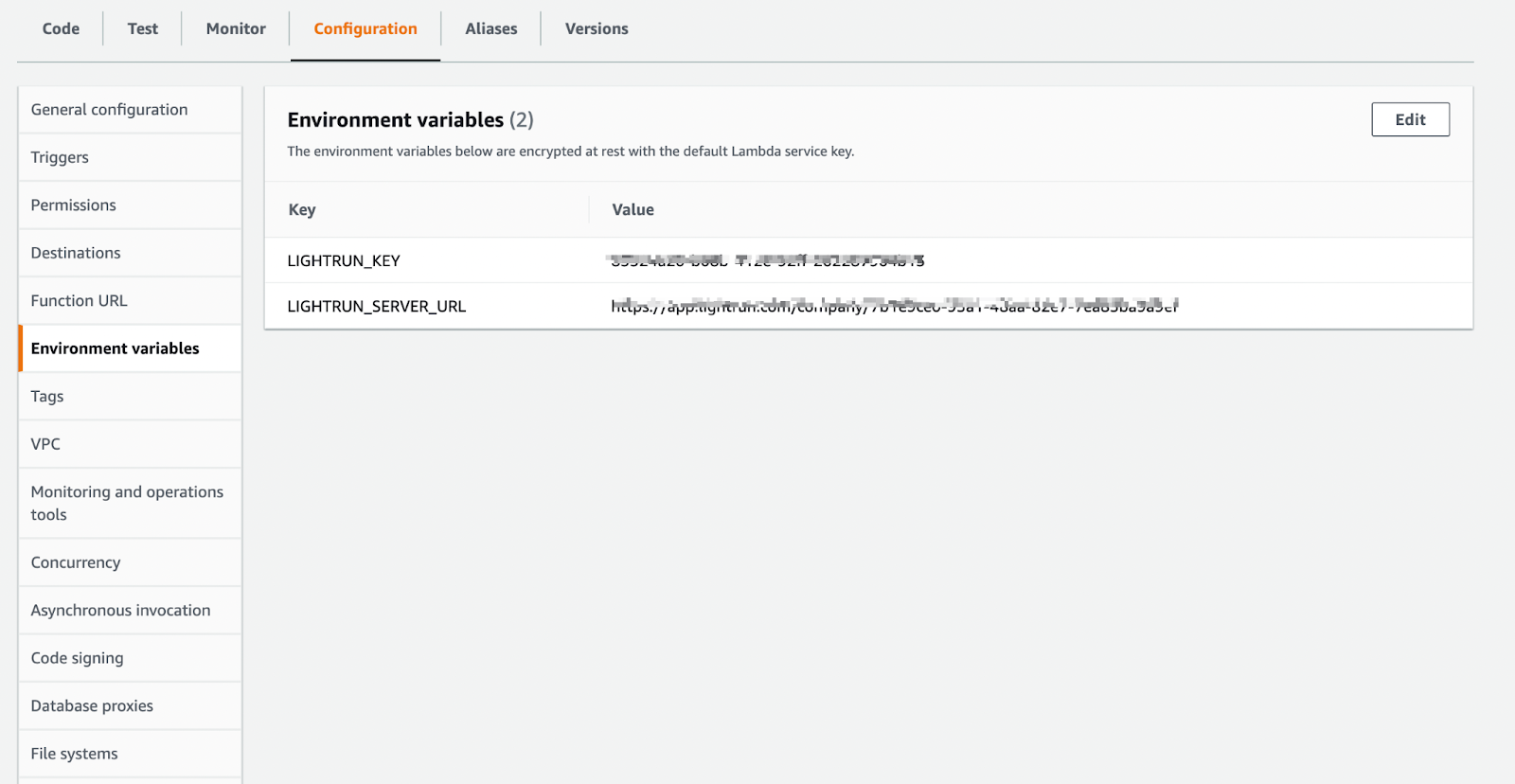
Click Configurations, select Environment variables, and click Edit to add a new environment variable. Set the variable names to LIGHTRUN_KEY and LIGHTRUN_SERVER_URL.
Note
You can get your LIGHTRUN_KEY and LIGHTRUN_SERVER_URL from your Lightrun Management portal.
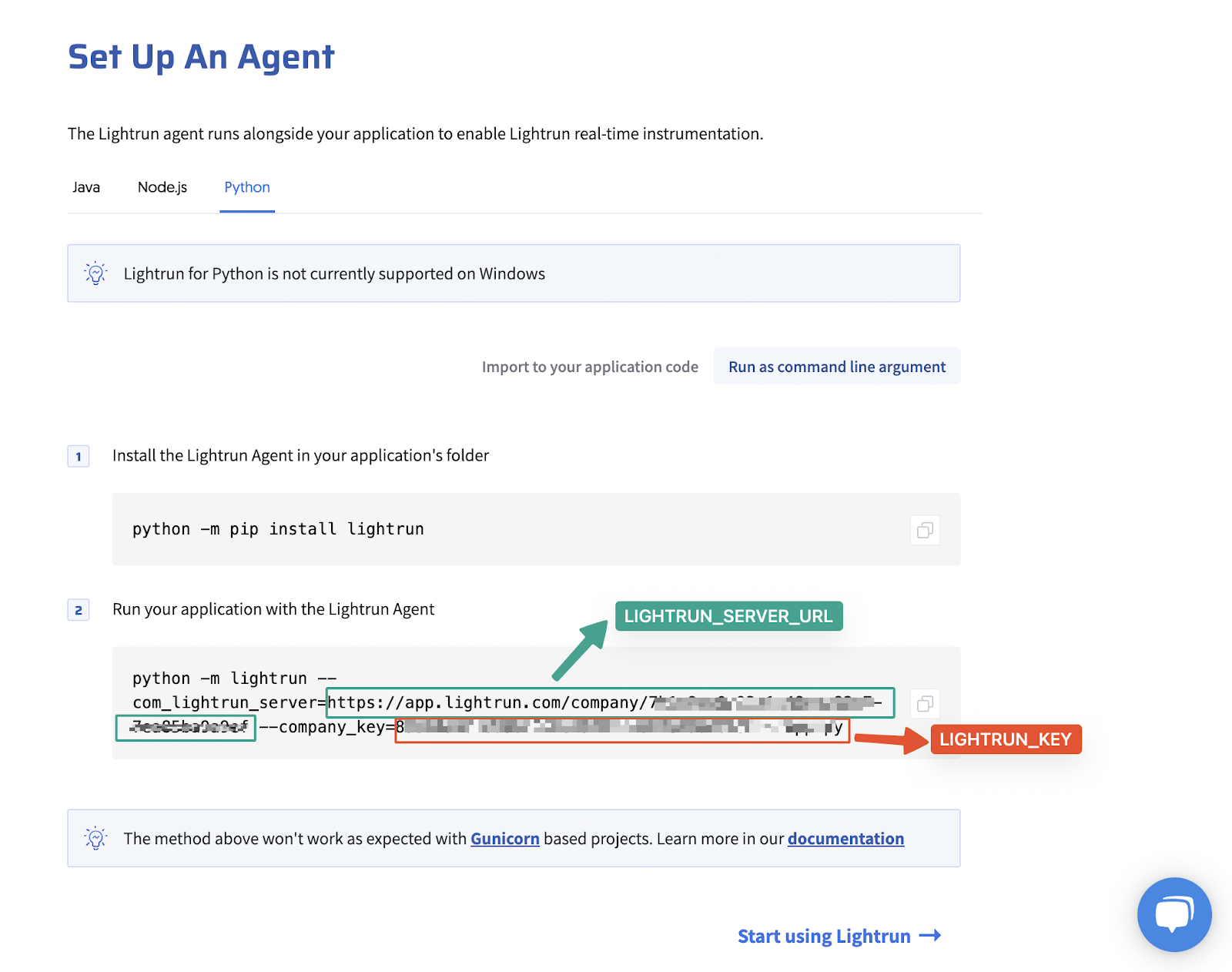
Then, add the following code samples to the function Code source.
import os
LIGHTRUN_KEY = os.environ['LIGHTRUN_KEY']
LIGHTRUN_SERVER = os.environ['LIGHTRUN_SERVER_URL']
def import_lightrun():
try:
import lightrun
lightrun.enable(com_lightrun_server=LIGHTRUN_SERVER, company_key=LIGHTRUN_KEY, lightrun_wait_for_init=True, lightrun_init_wait_time_ms=10000, metadata_registration_tags='[{"name": "<lambda-function-name>"}]')
except ImportError as e:
print("Error importing Lightrun: ", e)
Note
Change <lambda-function-name> to your Lambda functions name.
Important
AWS Lambda functions are event-driven short-running programs with a maximum execution time of 15 minutes. To debug AWS Lamda functions with the Lightrun Python agent:
-
Specify
lightrun_wait_for_init=Trueandlightrun_init_wait_time_ms=10000in the Python agent configuration. These two configuration parameters will ensure that the Lightrun agent starts up fast enough to work with the short-running AWS Lambda functions and also apply a wait time of about 10000 milliseconds before fetching Lightrun actions from the server. -
Apply Metadata tags that include the name of your Lambda function - By default, a new Lightrun agent is created whenever the Lambda function is invoked. By adding our function’s name as a metadata tag, we can attach Lightrun actions to agents created whenever the Lambda function is invoked, even before the Lambda function is invoked. This is because an action bound to a metadata tag is implicitly attached to all agents possessing that tag.
Call the import_lightrun() function in your lambda_handler function, and click Deploy to update the code source.
def lambda_handler(event, context):
import_lightrun()
Finally, to attach the Lightrun Python agent layer to the Lambda function, scroll down to the Layers section, and select Add a layer. Click Custom layers and select the appropriate layer from the drop-down list. Pick a version and click Add to attach the layer to your Lambda function.
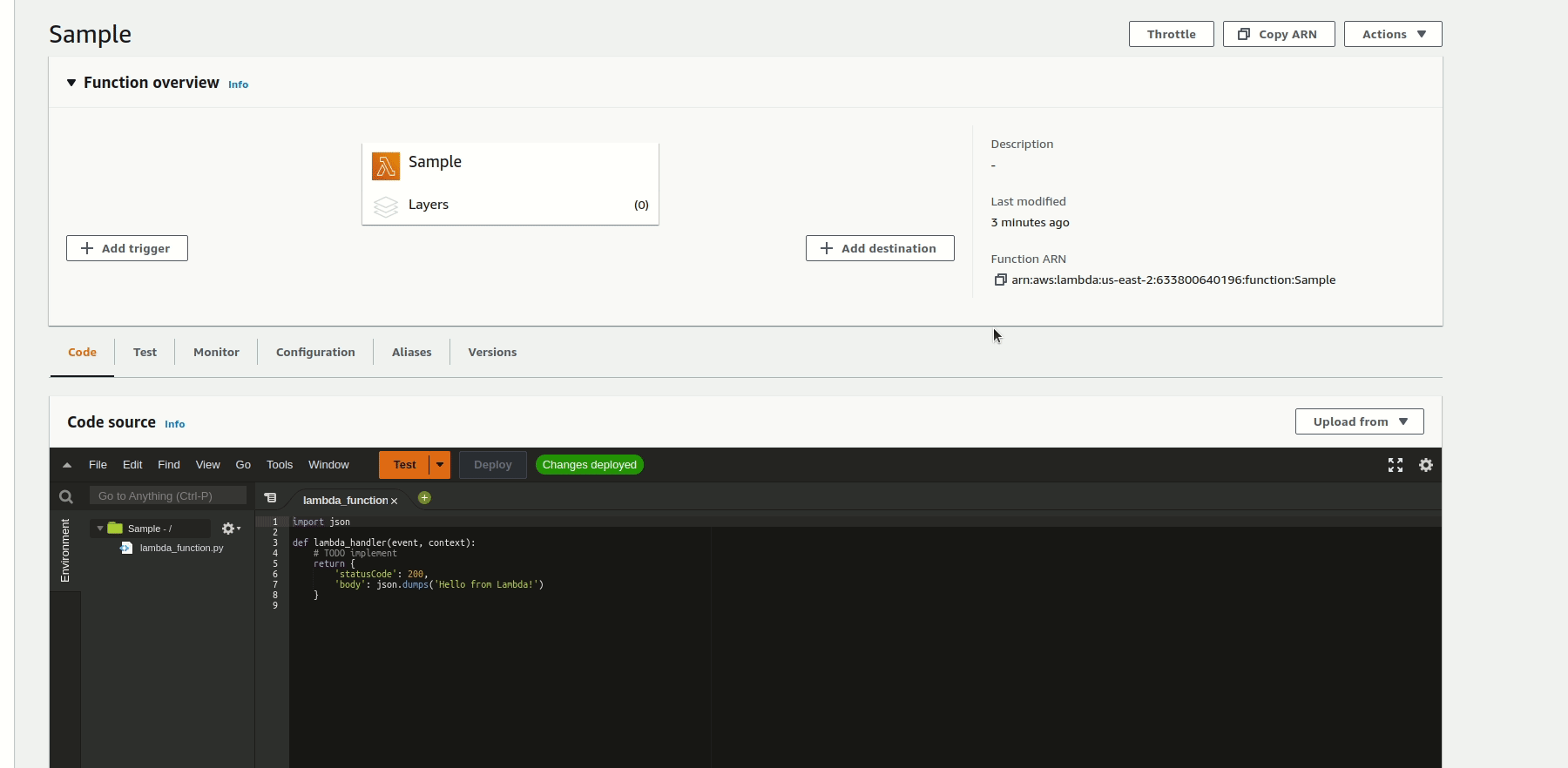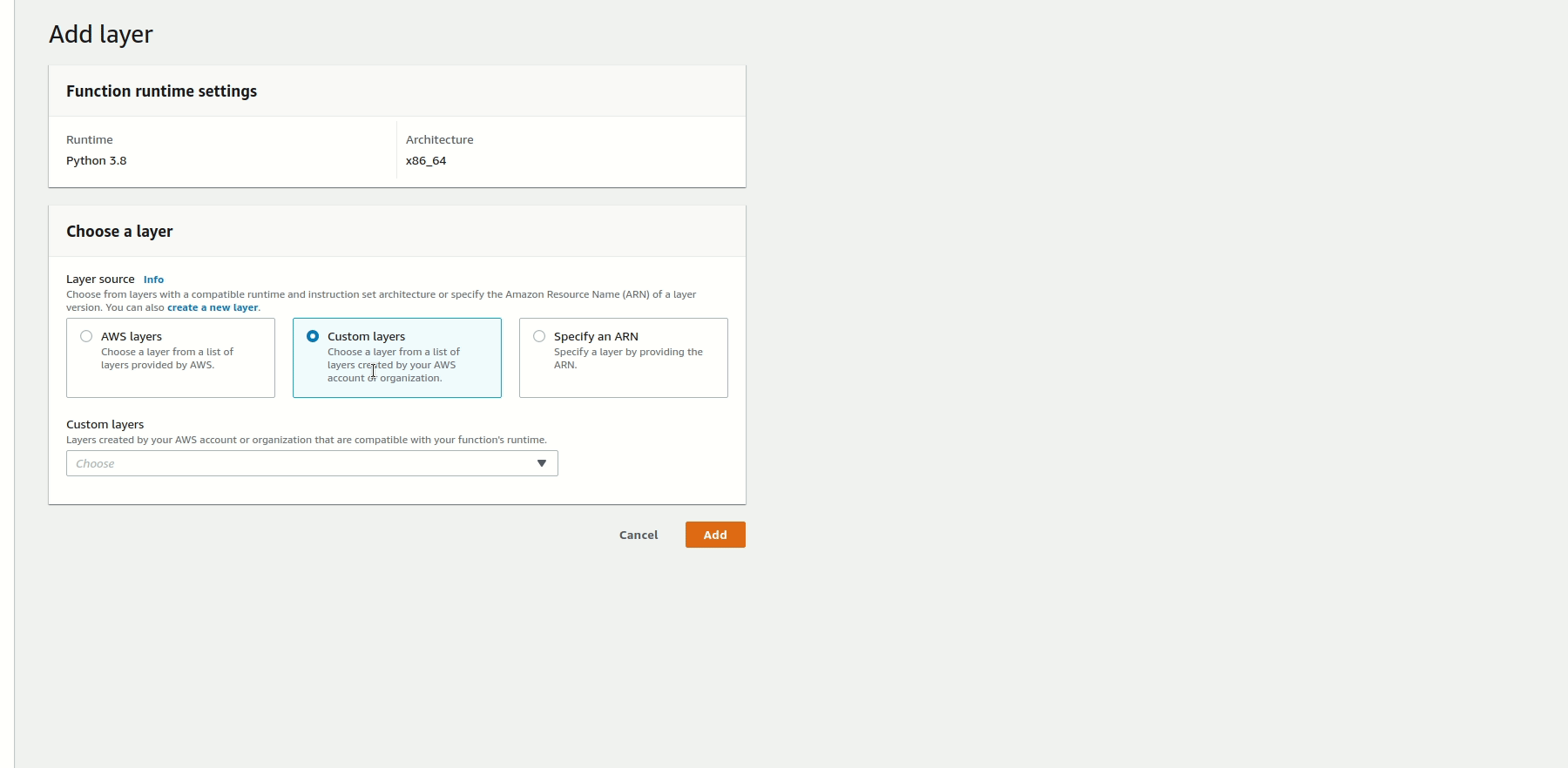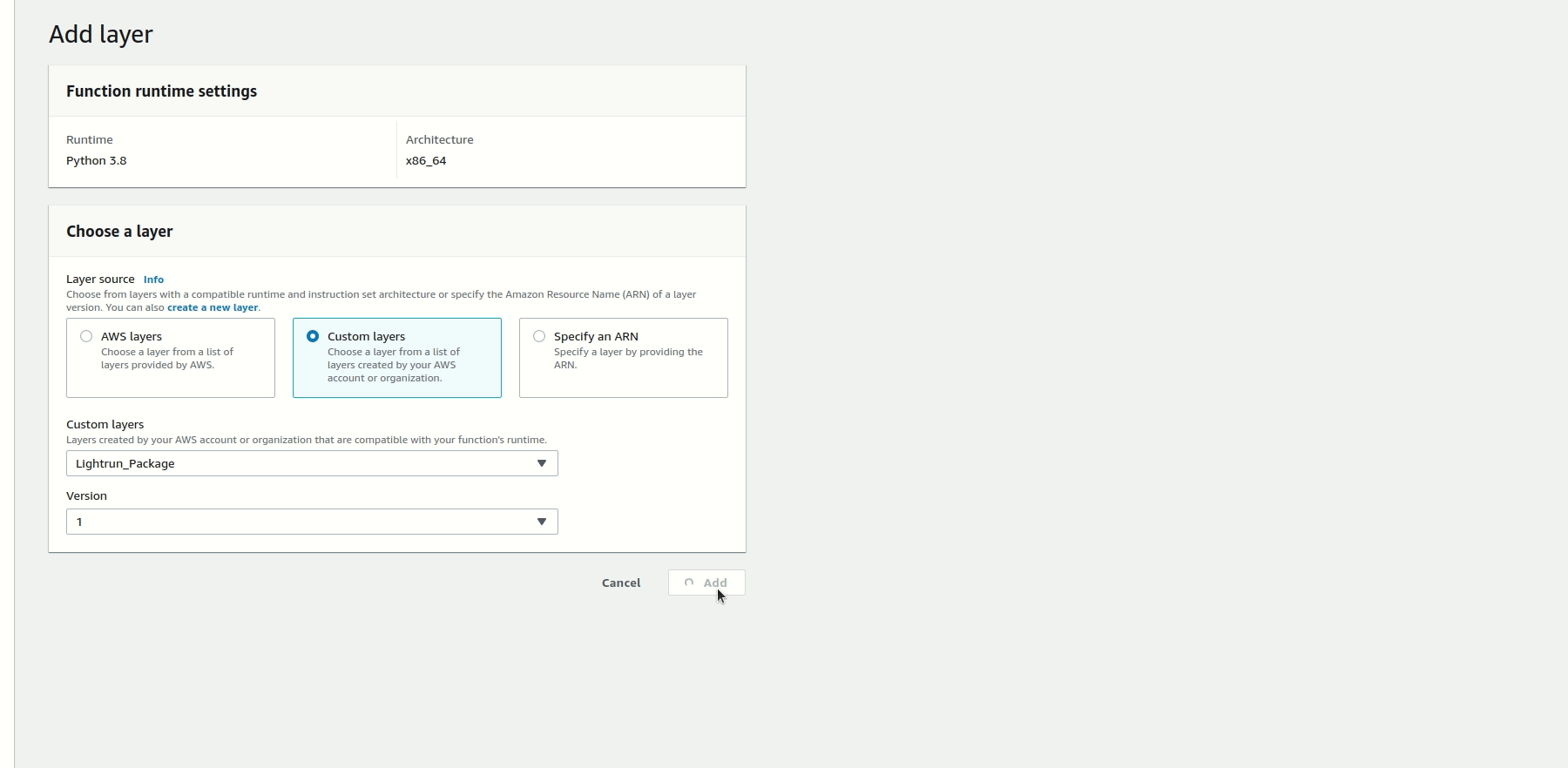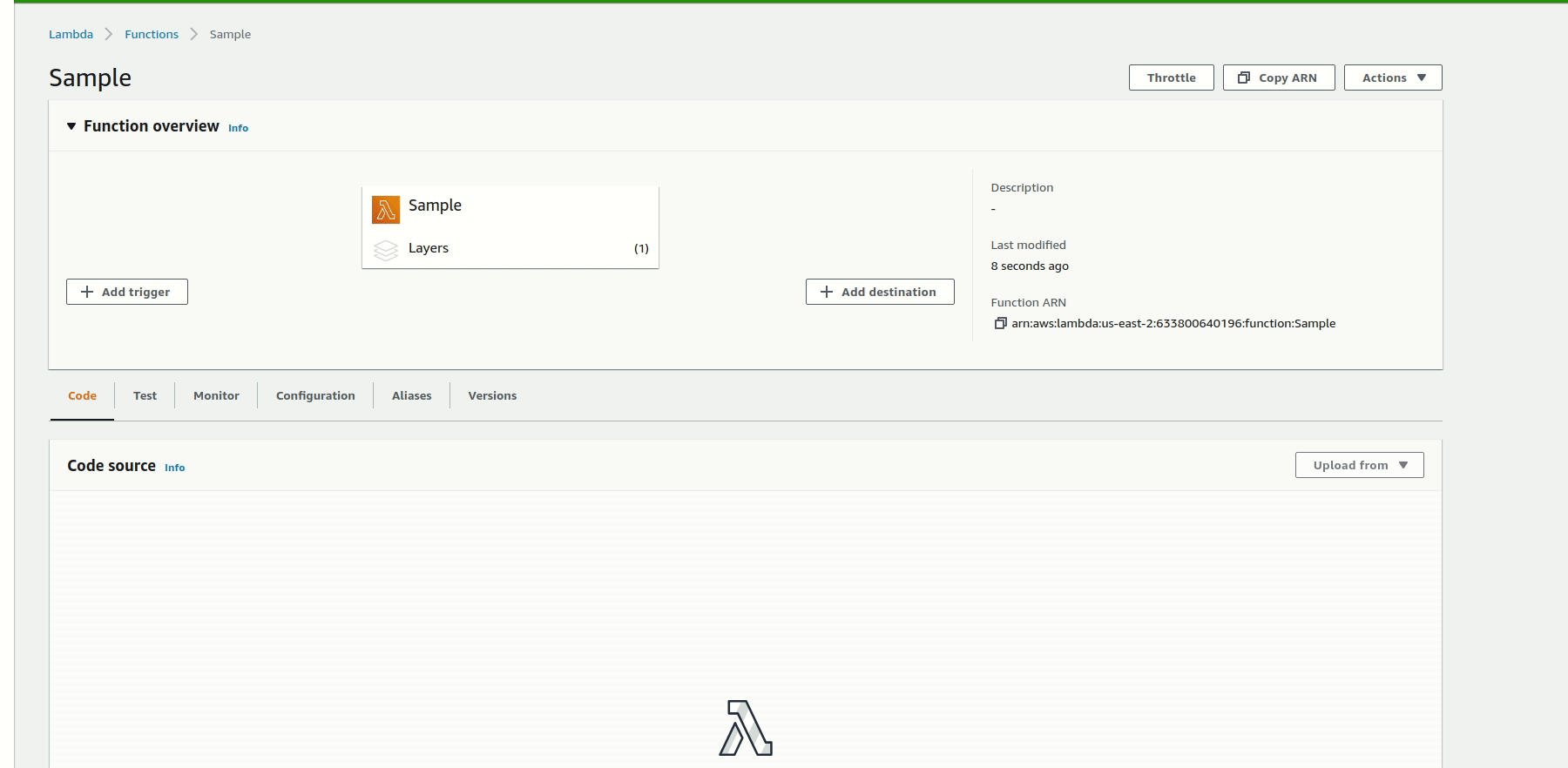
When you invoke the Lambda function, a Lightrun agent will be added to the Lambda function. You can confirm if the agent was added by checking your Lightrun Management portal.
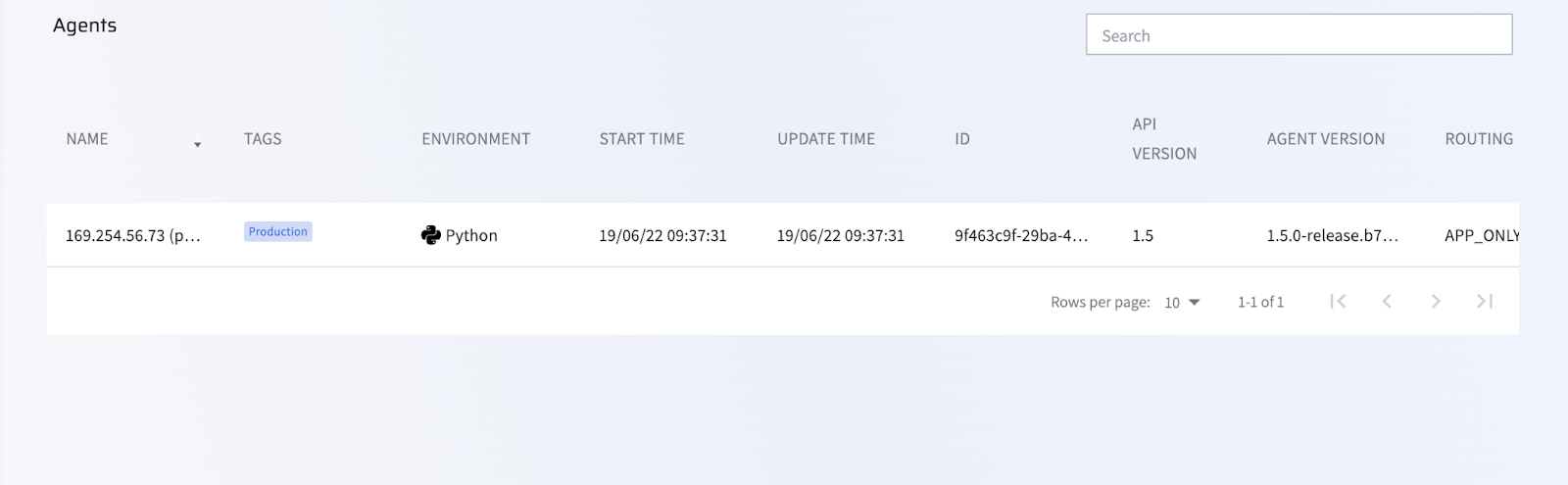
Add the Python agent Lambda layer to your application from the AWS CLI🔗
Note
- The following instructions assume that you have the AWS CLI installed on your local machine. Follow the instructions here to install and set up the AWS CLI on your local machine if you haven’t already installed it
- Ensure that you have configured all the permissions required to run an AWS Lambda function and created a Lamda execution role for the Lambda function. Learn more about the permissions needed to deploy a Lambda function here. Follow the instructions here to create a Lambda execution role for your Lambda function.
If you haven’t deployed your Lambda function to AWS, you can easily share the Lambda layer to your application during deployment with the AWS CLI. To demonstrate how to add the created Lambda layer to a Python function deployed with the AWS CLI, we will deploy a simple demo application as an AWS Lambda function with the Lambda layer added to it.
To create the demo application, create a folder for the application.
mkdir python_lambda_function
cd python_lambda_function
Add an index.py file to the folder.
touch index.py
Add the following code samples to the index.py file.
import os
LIGHTRUN_KEY = os.environ['LIGHTRUN_KEY']
LIGHTRUN_SERVER = os.environ['LIGHTRUN_SERVER_URL']
def import_lightrun():
try:
import lightrun
lightrun.enable(com_lightrun_server=LIGHTRUN_SERVER, company_key=LIGHTRUN_KEY, lightrun_wait_for_init=True, lightrun_init_wait_time_ms=10000, metadata_registration_tags='[{"name": "<lambda-function-name>"}]')
except ImportError as e:
print("Error importing Lightrun: ", e)
def start_fibonacci(n):
if n in {0, 1}:
return n
return start_fibonacci(n - 1) + start_fibonacci(n - 2)
def lambda_handler(event, context):
import_lightrun()
num = event['num']
print("Calculating Fibonacci of {}...".format(num))
return start_fibonacci(num)
Note
Change <lambda-function-name> to your Lambda functions name.
Important
AWS Lambda functions are event-driven short-running programs with a maximum execution time of 15 minutes. To debug AWS Lamda functions with the Lightrun Python agent:
-
Specify
lightrun_wait_for_init=Trueandlightrun_init_wait_time_ms=10000in the Python agent configuration. These two configuration parameters will ensure that the Lightrun agent starts up fast enough to work with the short-running AWS Lambda functions and also apply a wait time of about 10000 milliseconds before fetching Lightrun actions from the server. -
Apply Metadata tags that include the name of your Lambda function - By default, a new Lightrun agent is created whenever the Lambda function is invoked. By adding our function’s name as a metadata tag, we can attach Lightrun actions to agents created whenever the Lambda function is invoked, even before the Lambda function is invoked. This is because an action bound to a metadata tag is implicitly attached to all agents possessing that tag.
Finally, deploy the index.py file as an AWS Lambda function. You can do this in two ways.
- Deploy the
index.pyfile with .zip file archives. - Deploy the
index.pyfile as an AWS SAM application.
Deploy the index.py file as a .zip file archive🔗
First, to deploy the index.py file as a .zip file archive, zip the index.py file.
zip function.zip index.py
Then, deploy the function with the following command.
aws lambda create-function \
--region us-east-1 \
--function-name pythonapp \
--zip-file fileb://function.zip \
--role <lambda_execution_role_arn> \
--handler index.lambda_handler \
--runtime python3.9 --timeout 100 --memory-size 512 \
--layers <LayerVersionArn> \
--environment Variables="{LIGHTRUN_KEY=<key>, LIGHTRUN_SERVER_URL=<url>}"
Update the command with the following values:
--function-name- Lambda function name.--role- Lambda execution role ARN. (Follow the instructions here to create a Lambda execution role for your Lambda function.)--runtime- Preferred Python runtime environment.--layers- Lambda layer Version ARN--environment Variables- Lightrun secret Keys.
Note
You can get your LIGHTRUN_KEY and LIGHTRUN_SERVER_URL from your Lightrun Management portal.

If your deployment was successful, you should get a response similar to this.
{
"FunctionName": "pythonapp",
"FunctionArn": "arn:aws:lambda:us-east-1:<>:function:pythonapp",
"Runtime": "python3.9",
"Role": "<lambda_execution_role>",
"Handler": "index.lambda_handler",
"CodeSize": 528,
"Description": "",
"Timeout": 100,
"MemorySize": 512,
"LastModified": "2022-06-18T17:08:16.175+0000",
"CodeSha256": "oG5O0fLVyFDuygEXXcwG7AUkqmROCCMOJYAkPuWzzww=",
"Version": "$LATEST",
"Environment": {
"Variables": {
"LIGHTRUN_KEY": <key>,
"LIGHTRUN_SERVER_URL": <url>
}
},
"TracingConfig": {
"Mode": "PassThrough"
},
"RevisionId": "a0c151e7-ef8a-42aa-8574-813dc0e32f1d",
"Layers": [
{
"Arn": "<layer_version_arn>",
"CodeSize": 7911221
}
],
"State": "Pending",
"StateReason": "The function is being created.",
"StateReasonCode": "Creating",
"PackageType": "Zip",
"Architectures": [
"x86_64"
],
"EphemeralStorage": {
"Size": 512
}
}
Deploy the index.py file as an AWS SAM application🔗
Alternatively, you can deploy the index.py file by packaging it as an AWS SAM template.
Prerequisites
The following instructions assume that you have the AWS SAM CLI and Docker installed on your local machine. - Follow the instructions here to install the AWS SAM CLI on your local machine. - Follow the instructions here to setup Docker on your local machine.
Add a template.yaml file to the python_lambda_function folder.
touch template.yaml
Add the following yaml to the template.yaml file.
AWSTemplateFormatVersion : '2010-09-09'
Transform: AWS::Serverless-2016-10-31
Resources:
PythonApp:
Type: AWS::Serverless::Function
Properties:
Handler: index.lambda_handler
Runtime: python3.9
Role: <lambda_execution_role_arn>
Layers:
- <LayerVersionArn>
Environment:
Variables:
LIGHTRUN_SERVER_URL: <URL>
LIGHTRUN_KEY: <key>
Update the YAML file with the following values. - PythonApp - change to your preferred Lambda function’s name. - Role - Lambda execution role ARN. (Follow the instructions here to create a Lambda execution role for your Lambda function.) - Runtime - Preferred Python runtime environment. - Layers - Lambda layer Version ARN - Environment/Variables - Lightrun secret Keys.
Note
You can get your LIGHTRUN_KEY and LIGHTRUN_SERVER_URL from your Lightrun Management portal.

Run the following command to build the SAM template.
sam build
Run the following command to deploy the SAM template.
sam deploy --guided
And now you've added a Lightrun agent to your Python Lambda function! Install our plugin to get started adding Lightrun Actions to your application.